StackLeader Blog

Getting Started with AWS Lambda REST Services Part 3 of 3
Overview
Part 2 of this post outlined how to configure the AWS API Gateway so that the appropriate REST service could call the Lambda functions created in part 1. Part 3 of this post will detail the IAM configuration and deploying the API so that it is publicly accessible.
Securing API Gateway
Go to the API Gateway console.
https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/home
Select the Contact API created in part 2. Select /contacts->POST. Record the ARN.
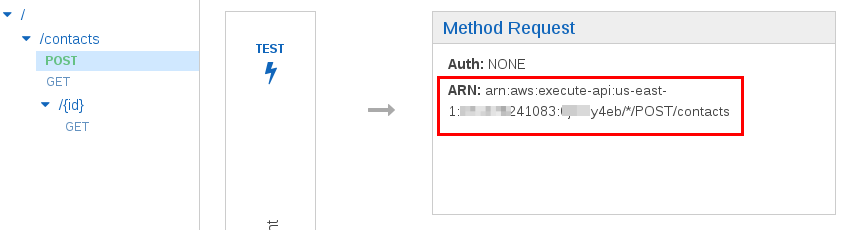
Select /contacts->GET. Record the ARN.
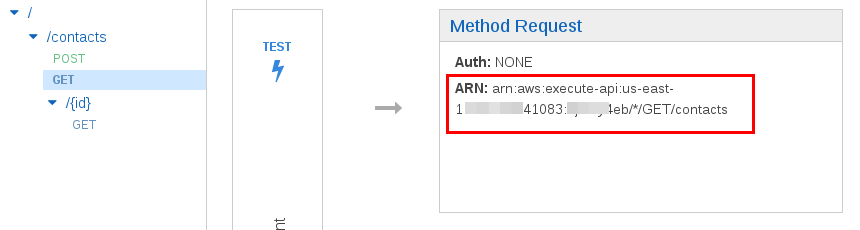
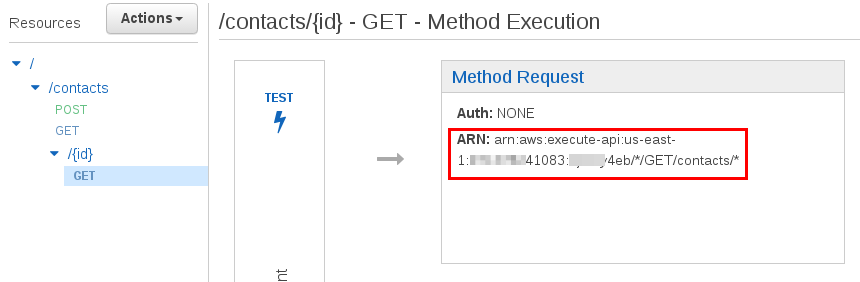
Select /contacts/{id}->GET. Record the ARN.
Select /contacts->POST->Method Request. Change Authorization to AWS_IAM.
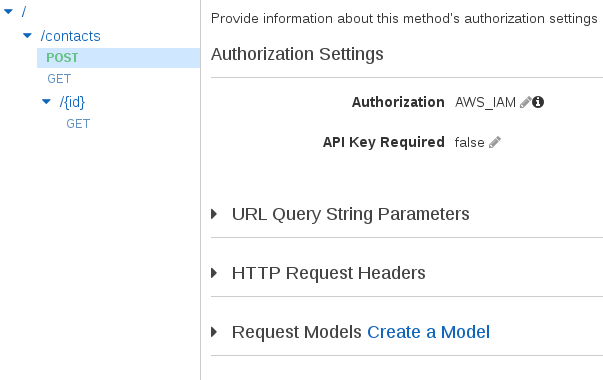
Change Authorization to AWS_IAM for endpoints /contacts->GET and /contacts/{id}->GET
IAM
IAM (Identity and Access Management) is a service in AWS that can create very granular security polices for services in AWS. We need to create two credentials. The first will only have access to making GET requests on the /contacts and /contacts/{id} endpoint. The second will only have access to POST to /contacts.
To get started, go to the IAM console.
https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home
Create Credentials
Go to Users->Create New User. Create two new users: contact-get and contact-post. Leave “Generate an access key for each user” checked.
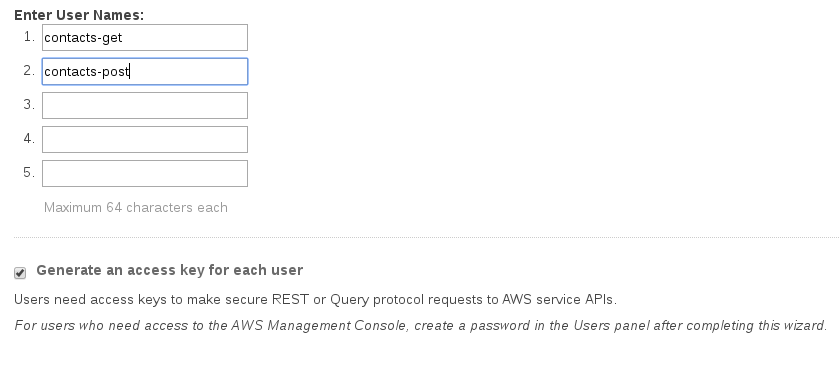
Save both of the credentials sets for later.
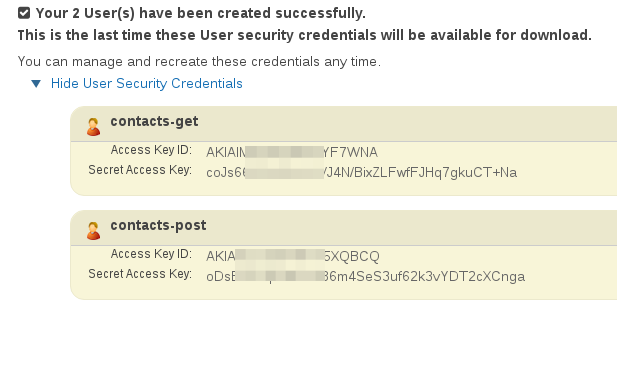
GET Security Policy
Select Users->contacts-get->Inline Policies->”…To create one, click here.” to create an inline policy. Select Policy Generator->Select. Set Effect to Allow, Service to Amazon API Gateway, Actions to Invoke, and set the Amazon Resource Name to the ARN of /contacts->GET and /contacts/{id}->GET. These ARNs where recorded in the Securing API Gateway section above. Separate the two ARNs by a comma e.g. arn:aws:execute-api:us-east-1:111111241083:aaaaaay4eb/*/GET/contacts, arn:aws:execute-api:us-east-1:111111241083:aaaaaay4eb/*/GET/contacts/*
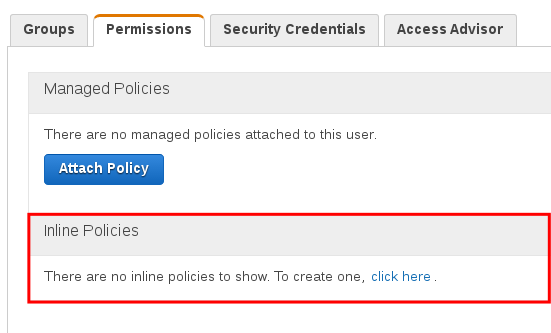
Note that these ARNs will be unique to your account. You must follow the Securing API Gateway section to get this part correct.
Select Add Statement.

Select Next Step->Apply Policy
POST Security Policy
Select Users->contacts-post->Inline Policies->”…To create one, click here.” to create an inline policy. Select Policy Generator->Select. Set Effect to Allow, Service to Amazon API Gateway, Actions to Invoke, and set the Amazon Resource Name to the ARN of /contacts->POST. This ARN was recorded in the Securing API Gateway section above.
Select Next Step->Apply Policy
Deploy API
Return to the Amazon Gateway API service. Select Actions->Deploy API. Set Deployment Stage to [New Stage] and set Stage Name to test.
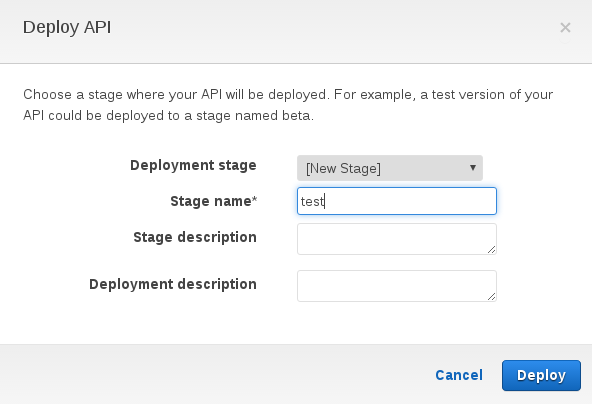
Select Deploy.
Test the API
Under Contact API->Stages->test record the Invoke URL
Open Postman. The installation of Postman is beyond the scope of this post.
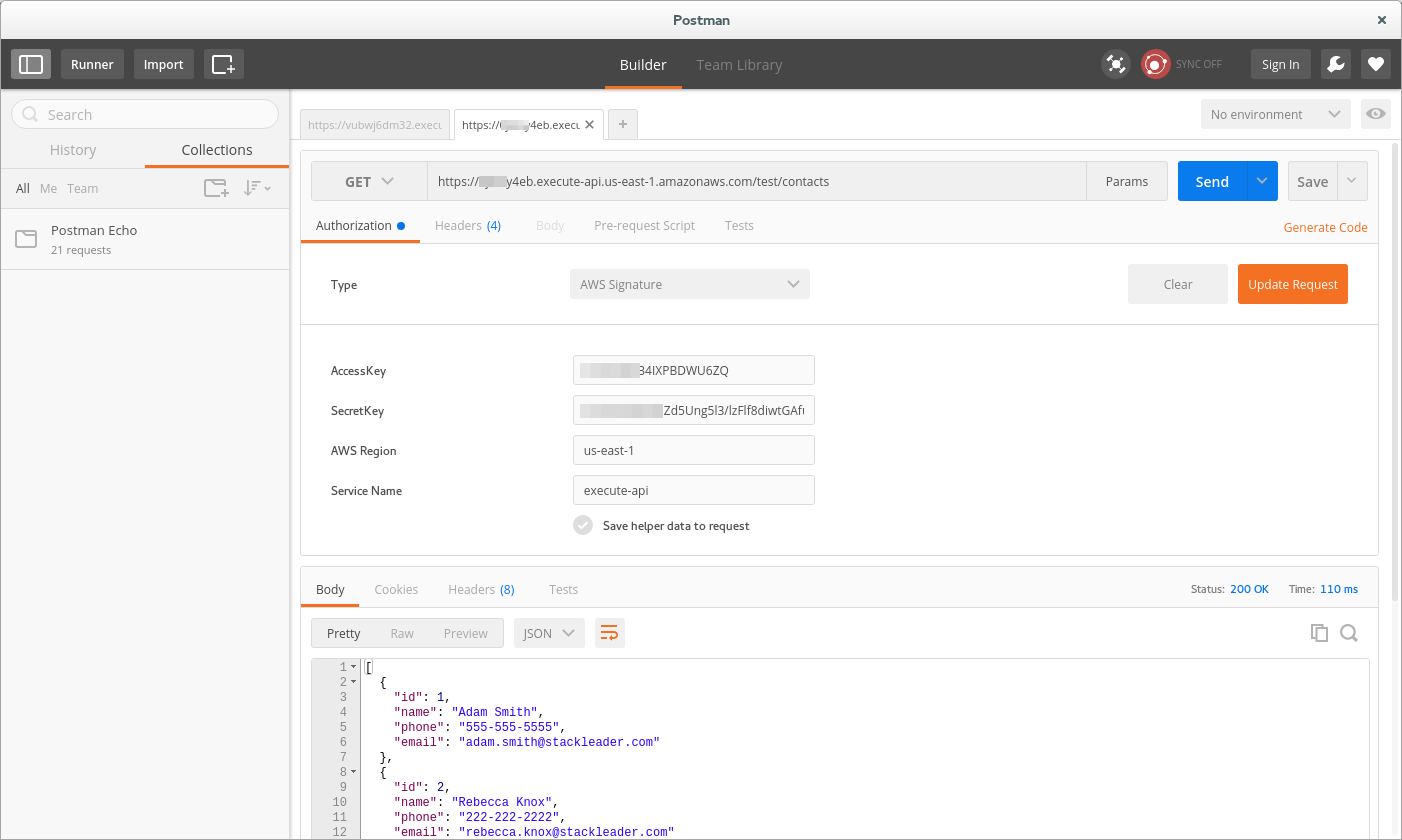
Set the method to GET, the URL to the Invoke URL copied from above. If the URL does not end in /contacts, add it e.g. https://111111y4eb.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/test/contacts. Under the Authorization tab set the type to AWS Signature. Set the accessKey and secretKey to the contacts-get users credentials recorded earlier in the post. Set the AWS Region to the region that the API Gateway was created in. The Invoke URL contains this information if you are unsure. Set the Service Name to execute-api. Select Update Requests and then Send. The response should contain a list of two contacts.
In Postman change the method type to Post. Select Body->raw and set the type to JSON (application/json). Set the body to:
{
"name" : "Adam Smith",
"phone" : "555-555-5555"
}Select Send. You should get a 403 forbidden since the AWS credentials are for contacts-get and this user does not have the right to POST.
Under Authorization, update the AccessKey and SecretKey to contacts-post which was recorded earlier in the post. Select Update Request and Send again. You should now get a contact in the response.